Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan template created by Ash Maurya that helps you deconstruct your idea into its key assumptions. It is adapted from Alex Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas and optimized for Lean Startups. It replaces elaborate business plans with a single page business model.
Business plans take too long to write, are seldom updated, and almost never read by others. Documenting your plan is key, and the Lean Canvas replaces long and boring business plans with a 1-page business model that takes 20 minutes to create and gets read.
In his 2010 book, Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers, author and Entepreneur Alex Osterwalder remarked : A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value. The business model is like a blueprint for a strategy to be implemented through organizational structures, processes, and systems. 3

Osterwalder highlighted 9 building blocks for building a sustainable business model which cover the four main areas of a business: customers, offer, infrastructure, and financial viability. The nine building blocks are:
1 . Customer Segments
An organization serves one or several Customer Segments.
- Value Propositions
It seeks to solve customer problems and satisfy customer needs with value propositions.
- Channels
Value propositions are delivered to customers through communication, distribution, and sales Channels.
4. Customer Relationships
Customer relationships are established and maintained with each Customer Segment.
- Revenue Streams
Revenue streams result from value propositions successfully offered to customers.
- Key Resources
Key resources are the assets required to offer and deliver the previously described elements . . .
- Key Activities
. . . by performing a number of Key Activities.
- Key Partnerships
Some activities are outsourced and some resources are acquired outside the enterprise.
- Cost Structure
The business model elements result in the cost structure.
- Problem and Customer Segments

In Running Lean: Iterate from Plan A to a Plan That Works, Entrepreneur and creator of the one-page business modeling tool “Lean Canvas“, Ash Maurya provides a step-by-step blueprint for practicing entrepreneurs who want to increase their odds of success. A business plan rests on a series of leap-of-faith assumptions, each of which can be tested empirically. Ash lays out his approach to breaking these assumptions down so that they can become the subjects of rigorous experiments.

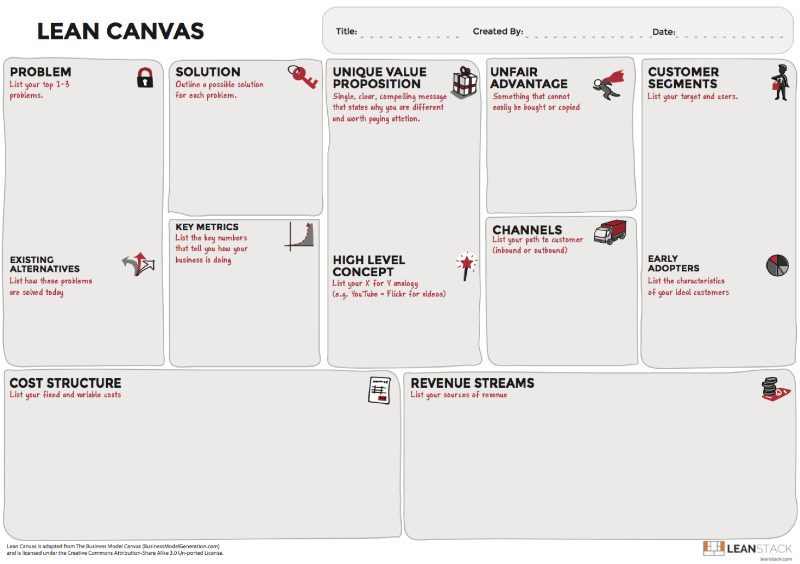
The Lean Canvas helps deconstruct your business model into nine distinct subparts that are then systematically tested, in order of highest to lowest risk. Lean Canvas is a business model validation tool. It’s a companion tool to this book that helps you document your business model, measure progress, and communicate learning with your internal and external stakeholders. 1
List the top one to three problems.
For the customer segment you are working with, describe the top one to three problems they need solved.
List existing alternatives.
Document how you think your early adopters address these problems today. Unless you are solving a brand new problem (unlikely), most problems have existing solutions. Many times these solutions may not be from an obvious competitor.
Identify other user roles.
Identify any other user roles that will interact with this customer.
Home in on possible early adopters.
With these problems in mind, get more specific on the customer segment. Narrow down the characteristics of your prototypical customer.
Your objective is to define an early adopter, not a mainstream customer.
Unique Value Proposition
Unique Value Proposition: Why you are different and worth buying getting attention.
Solution
“Bind a solution to your problem as late as possible.”
Because all you have are untested problems, it is fairly common for them to get reprioritized or completely replaced with new ones after just a few customer interviews.
Channels
Failing to build a significant path to customers is among the top reasons why startups fail.
“The initial goal of a startup is to learn, not to scale.”
Revenue Streams and Cost Structure
The “Revenue Streams” and “Cost Structure,” are used to model the viability of the business.
“Use the revenue streams and cost structure inputs to calculate a break-even point and estimate how much time, money, and effort you need to get there.”
Key Metrics
Every business has a few key numbers that can be used to measure how well it is performing. These numbers are key for both measuring progress and identifying hot spots in your customer lifecycle.
Unfair Advantage
A real unfair advantage is something that cannot be easily copied or bought by your competitors.
Looking to build your successful tech Startup? Join our 12-week cohort of tech startups for Black founders by Black industry experts.